Much like the game, the US Army’s Computer Hardware, Enterprise Software and Solutions (CHESS) fathoms many a seasoned contractor. This article is a guide to everything there is to know about CHESS and the latest developments in the procurement tools housed within CHESS.
According to AFARS 5139.101-90 (a), “…Purchasers of commercial hardware and software must satisfy their IT requirements by utilizing CHESS contracts and DoD enterprise software agreements first, regardless of dollar value.” The program has a clear vision – to achieve excellence in meeting Army and DoD policies by way of offering competitive contracts that provide both value-added, economical and Networthy IT products and superior, performance-based IT services. IT contracts within CHESS are established in accordance with HQDA CIO/G-6 standards and policies.
To achieve this vision, CHESS was founded in 1996, as per the Clinger-Cohen Act, as a product under PEO Enterprise Information Systems (PEO EIS), with supervision by the Assistant Secretary of the Army for Acquisition, Logistics and Technology (ASA ALT), who directly reports to Enterprise Services (ES). At its conception in 1996, sales for Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) goods through CHESS reached a peak of $363 million. However, it wasn’t until 2009 that CHESS gained traction across all functional areas, when a memo released by ASA ALT solidified the importance of the savings and benefits that could be accrued from it.
Many a famous IDIQ resides within CHESS, some of which are open to other federal agencies. However, its many intricacies have impeded agencies from doing so. The following information may shed some light.
Organization
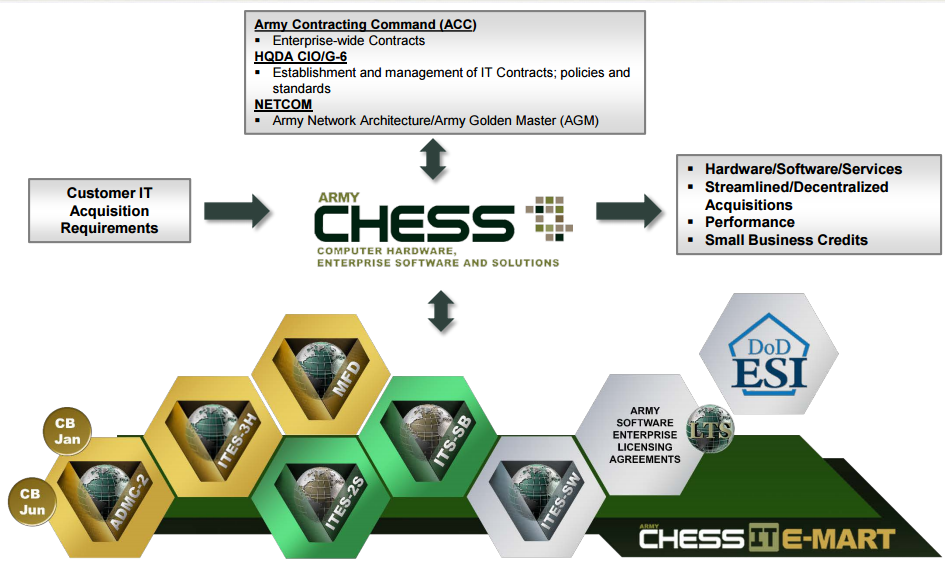
The CHESS system is roughly divided into hardware (ADMC-3/ADMIC-2, ITES-3H, and MFD), services (ITES-2S, and ITS-SB), and software (ELA, ESI, and ITES-SW). This article will focus on hardware.
o ADMC-3 and ADMC-2
The hottest component within the hardware section of CHESS in 2016 is ADMC-3. The Army Desktop and Mobile Computing-3 (ADMC-3) IDIQ (Sol#W52P1J-15-R-0122) is set up to provide commercial-off-the-shelf IT equipment, which is managed and administered by the U.S. Army Computer Hardware, Enterprise Software and Solutions (CHESS). It has a ceiling of $5 billion and a 4 Year Base with three 2- year options, totaling up to a 10 year ordering period.
ADMC-3 will operate under the approved NETCOM Army Golden Master (AGM) desktop operating system and application suite image. The Army Gold Master (AGM) is a NETCOM managed evolving suite of software that will be required to be loaded by the contractors on all Army PCs, workstations, servers, and notebooks. After all responses are received, 8 awards will be given out for ADMC-3. The IDIQ’s predecessor, ADMC-2 doled out 8 awards to the following companies: Dell, CDW-G, HP, ITG, Transource, Emtec, Telos, and NCS.
Up to 5 of the 8 awards are reserved for small businesses. According to the final request of proposals, released May 3rd, 2016, all Delivery Orders valued between $3,000.00 and $150,000.00 shall be set-aside for Small Business, in accordance with FAR 19.502-2. The guaranteed minimum on this contract is $10,000. The award date for ADMC-3 is anticipated to be the 2nd quarter of FY2017. Furthermore, after the contract award, the bidder’s performance under this contract will be subject to an assessment(s) in accordance with FAR 42.15 and AFARS 5142.1503-90. Ratings after the assessment range from Dark Blue (Exceptional) to Red (Unsatisfactory).
In addition, these contracts will be awarded to a set of lowest prices that are acceptable, depending upon the item. The awarded contracts will act as a procurement site for the Army’s Consolidated Buy (CB), an initiative that aims to reduce Army costs and standardize IT enterprise. Such standardization is crucial as it simplifies the process of security updates and patch management. In addition, Consolidated Buy is expected to save the Army $445.71 million, while generating high-volume sales totaling at a whopping $1.10 billion
Three CBs shall be run over the course of a year; CB-1, CB-2 and CB-3 for a duration of four months each. Dates of these CBs are from 1 October through 31 January, 1 March through 30 June, and from 1 July through 30 September. These include technology refreshment, replacement and new technology provisions. Contractors shall have the opportunity to refresh product offerings before each CB period. During CB-1 cycle, and every third CB cycle thereafter (e.g., CB-4, CB-7, CB-10, etc.), the complete product offering of the ADMC-3 contract shall be offered. Product offerings during these CB periods shall establish the vendors ceiling prices for each product category and will be enforced the remainder of the year (i.e., next two CB periods).
The latest CB period is CB-23. The ordering dates for CB-23 are 13 June through 30 September 2016. CB-23 will offer DOD Win10 compliant platforms. The approved Army Golden Master (AGM) for CB-23 will be Windows 7/64 Bit for desktops/laptops, and Win 8.1/64 Bit for tablets/slates. In preparation for the upcoming release of Win10 OS/AGM, CB users are recommended to prioritize the purchase of desktops and laptops containing TPM 2.0 chips, IAW NETCOM Technical Authority (TA) guidance. The next CB, CB-24, will start on 17 June 2017 and end 31 March 2017.
ADMC-3 is followed by its own controversy. In October 2015, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) restricted all government purchases of laptops and desktops to three MACs, which are NASA’s SWEP, GSA’s Schedule 70, and NIH’s CIO-CS. The restriction was an effort to enforce category management policy for desktops, laptops, and the like. The Army initially sought to procure its IT needs through SWEP V. This, however, did not happen due to SWEP V protests as well as the Army’s own internal delays. The flight from OMB’s guidance solidifies the army, for now, with a contract vehicle that is solely theirs, making ADMC-3 extremely lucrative for both large and small companies.
o ITES-3H/ ITES-2H
Information Technology Enterprise Solutions-3 Hardware (ITES-3H) is one of the other illustrious IDIQs of 2016. With a $5 billion ceiling and a period of performance from 25th of April 2016 to the 21st of February 2021, the IDIQ has 17 contracts to offer. Of the 17, 8 are solely designated to small businesses. It is open to Army, DoD and other federal agencies.
ITES-3H’s scope includes IT hardware solutions of COTS, which include Windows-based servers, storage systems, video-teleconferencing equipment, RISC/EPIC servers and so on. Other related fixed price services under ITES-3H include legacy equipment maintenance (which might change soon hyperlink to article) , system configuration and integration and the like. Also included are provisions for new technology and technology refresh.
In early February, the Army picked 8 large companies (CDW-G, Vernon Hills, Ill., Dell, GovConnection; Rockville, Md., Hewlett-Packard Enterprise, IBM Corp., Telos; Ashburn, Va., Unicom; Herndon, Va., World Wide Technology, St. Louis, Missouri (W52P1J-16-D-0016)) and 7 small companies (Affigent; Herndon, Va., Dynamic Systems; El Segundo, Calif., Force3; Crofton, Md., Government Acquisitions; Cincinnati, GTRI; Denver, Intelligent Decisions; Ashburn, Va., Iron Bow; Chantilly, Va., MicroTech; Vienna, Va., Wildflower; Santa Fe, N.M.). 50 bidders were put though two competition phases, during which the Army filtered out those that did not meet pre-requisites. The Army accounted for 80% of the business within ITES, even when the contract was open to other government buyers. The winners will now compete for task orders to provide servers, laptops, and other iT products to buyers.
The contract, originally to be awarded in 2014, was delayed due to its predecessor, ITES-2h, which has had its own share of protests and controversy. The $20 billion, 9 year contract was bombarded with protests in April 2006, after awarding 11 large and small contractors. The GAO sustained protests by five companies, citing that the Army failed to hold productive discussions with bidders, while also evaluating proposed labor rates in an unreasonable manner. The Army then did what it does best, divide and conquer, it allowed the five protesters — BAE Systems North America, Northrop Grumman, NCI Information Systems, Multimax and Pragmatics — to join the contract. Since the protests, over $1 billion has been added to its ceiling.
Additionally, the CHESS contracts designated for DOD UC APL item acquisitions are under the Information Technology Enterprise Solutions-3 Hardware (ITES-3H) Program. The DOD UC APL items should be acquired by soliciting proposals from the ITES-3H contractors. These contractors are:
CDW-G Dell
Unicom World Wide Technology (WWT)
Affigent Telos
IBM Dynamic Systems
Hewlett Packard Wildflower International
GovConnection Force 3
Government Acquisitions Intelligent Decisions
Microtechnologies
The acquisition of IA APL products will be IAW competition requirements and the ‘Related Items CLIN’ (0010) of the basic ITES-3H contracts.
o MFD
With a program maximum of $489 million and a three year period of performance, ending October 31st, 2016, the Multifunctional Device contract encompasses purchase of MFD equipment, accessories, maintenance plans and associated consumable supplies; leasing of MFD equipment, accessories, maintenance plans and consumable supplies, to include Operating Lease and Lease-to-Own arrangements; Cost-per-Copy arrangements that include equipment, accessories, maintenance and supplies; all labor, transportation, parts, equipment and all required supplies (except paper, staples and binding tape), necessary for operation of digital MFDs.
The contract also involves installation, de-installation (during turn-in inspection/removing equipment), maintenance, repair and/or replacement, hard drive removal, training and diagnostic service calls to tenant units at CONUS Army installations and Army CONUS sites. Ordering is open to CONUS Army customers or other DOD customers located on Army installations and are available to use for equipment connecting to an Army network.
Current contract holders include 6 large businesses (XEROX Corp., Canon USA, Inc. , Ricoh USA, Inc., Konica-Minolta Business Solutions, Lexmark International, and KST Data, Inc) and, one small business (Cartridge Technologies Inc (CTI)).
After it’s expiry on the 31st of October, 2016, MFD requirements must be fulfilled under ITES-3H, which allows purchase and lease of COTS IT hardware. Existing DOs up to 60 months will be honored under MFD. Upon completion, follow-on activity must be procured from ITES-3H.
To summarize, the flowchart here outlines the lines the way a customer would go about to procure hardware through CHESS.
Check out our guide to Services and Software Procurement here!
Want to know more? Attend an informational session.



